For any business, big or small, data has always been considered an essential part of the IT infrastructure in supporting their daily operations. Companies today are keen on choosing the best systems to manage online applications but put less focus on implementing a system for data protection. A data loss could mean a business loss, businesses should ensure data protection by adding RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) to the storage configuration.
If you are planning to set up a RAID system but confused about how to choose the right one? RAID is one of the best solutions for businesses and high-end workstations available for protection of valuable data. For software or hardware implementation, RAID supports single disk failure, however RAID may not be the perfect system for ongoing data security.
What is RAID and Why Is It Important?
RAID is a data storage virtualization technology that combines multiple physical disk drive components into one or more logical units for the purposes of data redundancy, performance improvement, or both.
In this day and age, every business needs to store a huge amount of client data including their names, date of birth, contact information, financial information and more. If you store these data in a multiple drive without using RAID, there are chances of backup failure due to an unexpected failure in the hard drive. Implementing RAID is an efficient way to make a storage system more reliable, and it may improve system performance as well.
Various RAID Levels that Cater for Your Business Requirements
The RAID level you use would affect the speed and fault tolerance you can achieve from RAID. RAID 0 is the fastest, RAID 1 is the most reliable and RAID 5 is considered a good combination of both. It also matters whether you have software or hardware RAID as software supports fewer levels than hardware-based RAID. Below is a deeper dive at each of the RAID levels:
RAID 0 – Striping
RAID 1 – Mirroring
RAID 5 – Striping with Parity
RAID 6 – Striping with Double Parity
RAID 10 – Combining Mirroring and Striping
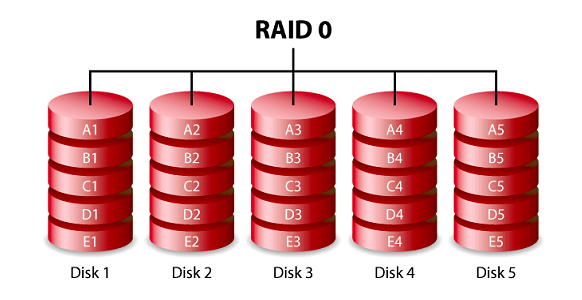
RAID 0
RAID 0 configuration provides disk striping across all drives in the RAID drive group, which offers maximum performance among all RAID levels. Since there is no RAID overhead all drives can be combined to a single logic disk. The biggest disadvantage of RAID 0 is that there is no data protection, which means that a failure in a single drive could result in total data loss.
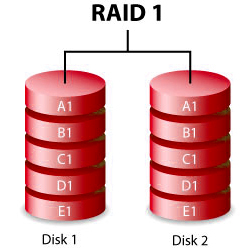
RAID 1
RAID 1, or known as disk mirroring, is the process of replicating the data to more than one disk. It is a standard that can improve the security of stored data. The concept relies on a network of two or more hard disks to store data in a mirrored manner.
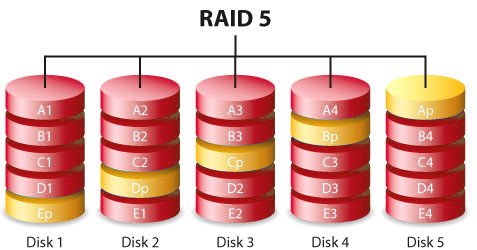
RAID 5
RAID 5 uses multiple hard drives in an array and distributes parity data across all drives to improve reliability. Unlike RAID 0, the data is interspersed with parity bits in case of the event of a hard disk failure. The data on the failed component can be rebuilt from the distributed data and parity information on the other components.
RAID 6
RAID 6 is similar to RAID 5, but the parity data are written to two drives only. In other words, it requires at least 4 drives and can withstand two drives fail simultaneously. Even if two disks die at the same time, RAID 6 can reconstruct the data with the double parity, and makes RAID 6 highly secure and fault-tolerant.
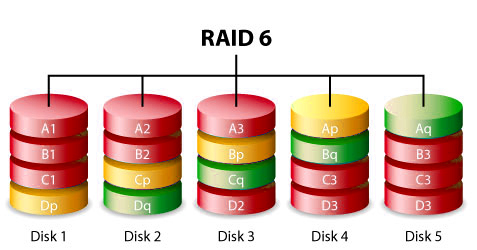
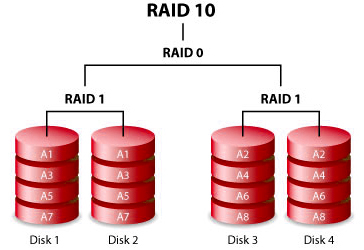
RAID 10
RAID 10 is a combination of RAID levels 1 and 0, whereby multiple RAID 1 systems are combined with a RAID 0 setup. That is why RAID 10 is also frequently referred to as “RAID 1 + 0”. RAID 10 always consists of at least four hard disks.
Comparison of the RAID Levels
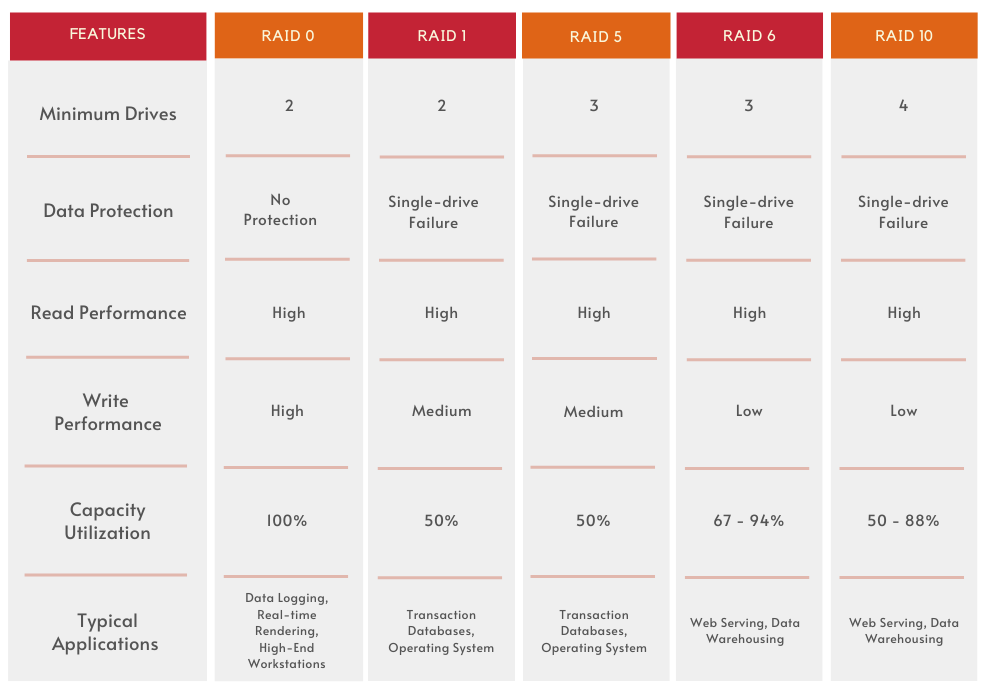
Which RAID Level Suit Your Business Most?
For most SMEs, RAID 5, RAID 6 and RAID 10 are sufficient for good performance and fault tolerance. For limited-budget users, we would recommend RAID 5 and 6 to get the most out of the disks.
To conclude, if your company suffers due to corrupted data, there are chances to recover the lost data by repairing the damaged disks. RAID recovery software rebuilds damaged arrays in software, hardware and configurations. You may also refine a Google search to select the right software for resurrecting the damaged data.